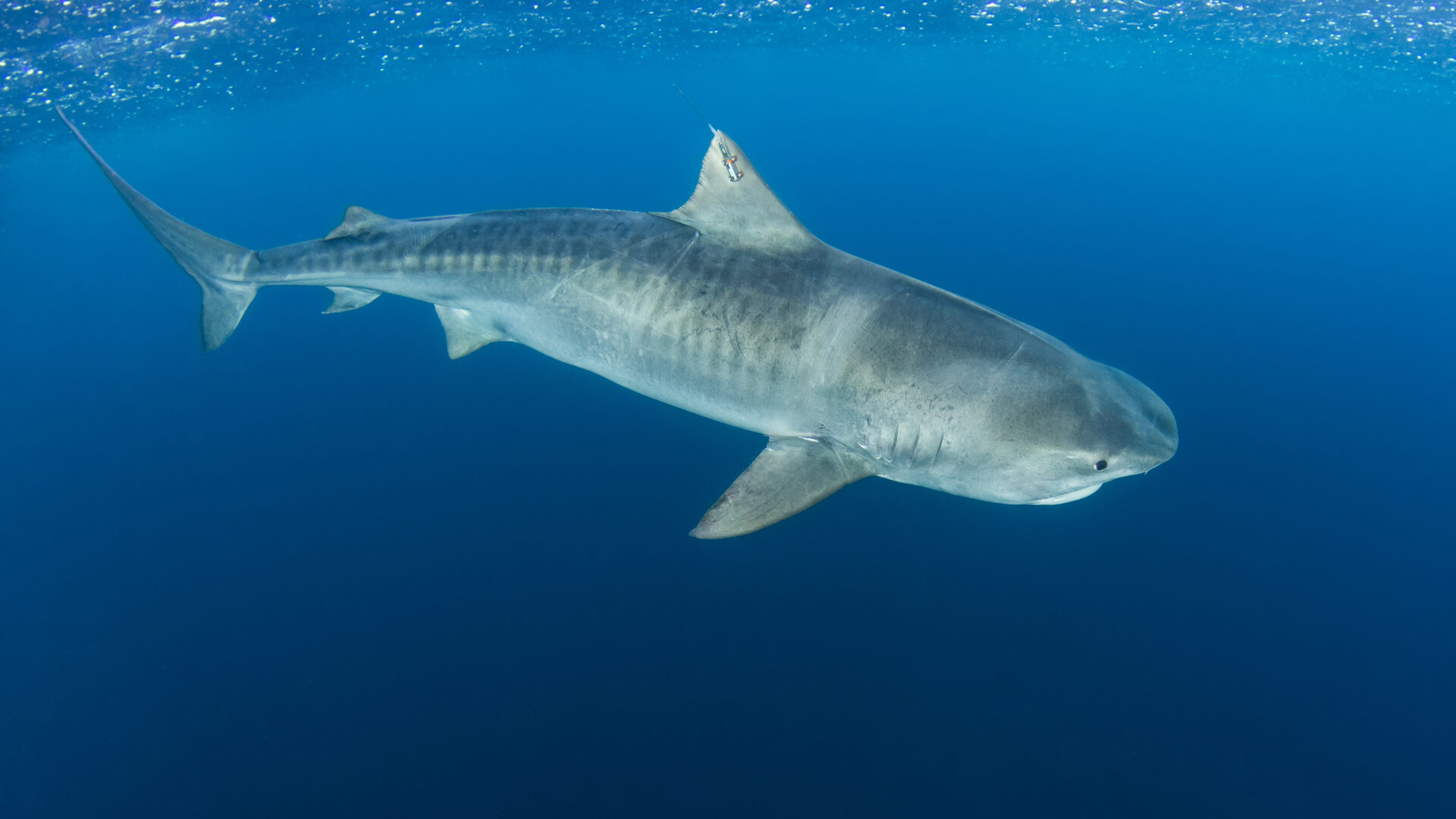
July 31st – August 7th, 2021 – For the first time on the Saba Bank, an expedition team was able to successfully assess the shark diversity by attaching five satellite tags and confirming pregnancy stages by ultrasound of two species of sharks. This research advancement resulted in assessing 56 sharks, including 16 Tiger sharks with one confirmed early-stage pregnancy, and the first tagged male in the region. These details inform us that the Saba Bank’s important role in the shark populations of the North-Eastern and wider Caribbean Region have yet to be unlocked. This information is crucial to better protect sharks within the Dutch Caribbean’s Yarari Marine Mammal and Shark Sanctuary as well as beyond.
Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance (DCNA) along with the Protected Area Management Organizations of the Dutch Caribbean: Saba Conservation Foundation (SCF), Nature Foundation St. Maarten (NFSXM), St. Eustatius National Parks (STENAPA), STINAPA Bonaire, the Aruba National Parks Foundation (FPNA), the Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance (DCNA) and World Wildlife Fund for Nature- The Netherlands (WWF-NL) led a team on the Saba Bank in collaboration with Arizona State University, University of Groningen, Beneath the Waves and funded by the Biodiversity Fund of the World Wildlife Fund for Nature- The Netherlands (WWF-NL) .
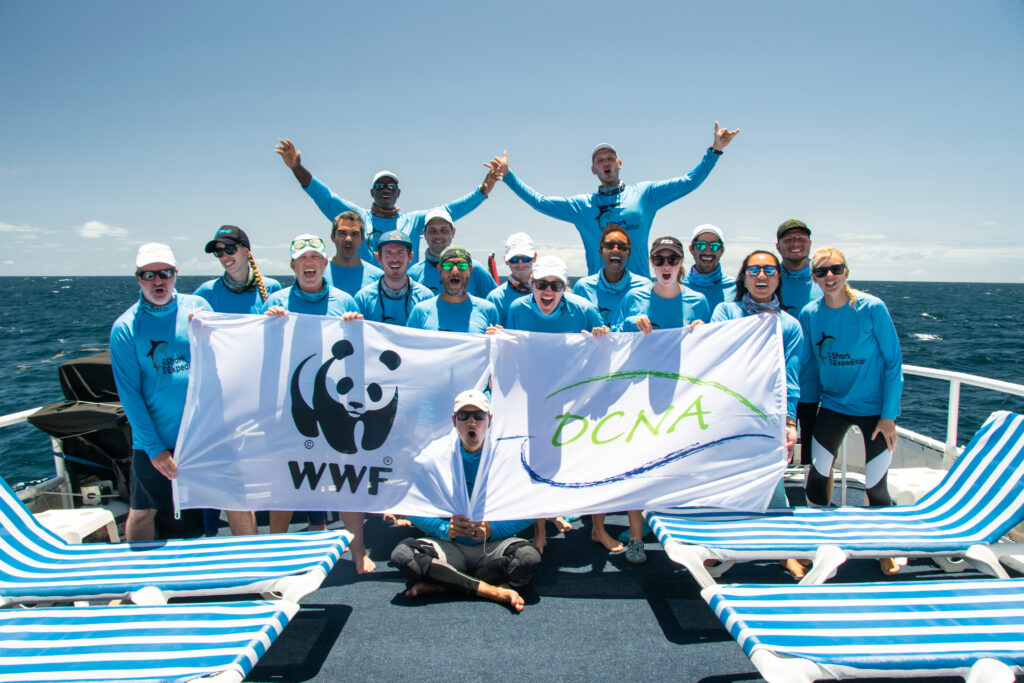

This week-long ocean research expedition aimed to understand the stages of the reproductive cycle of tiger sharks on the Saba Bank. Tadzio Bervoets, Director of DCNA and expedition leader adds “It is critical to collect the data necessary to advance the conservation actions for species of sharks in the Caribbean Region and with the data collected over the last week we have been able to get a clear picture of the important role the Saba Bank plays”. This expedition built upon previous research and expertise from collaborating scientists.
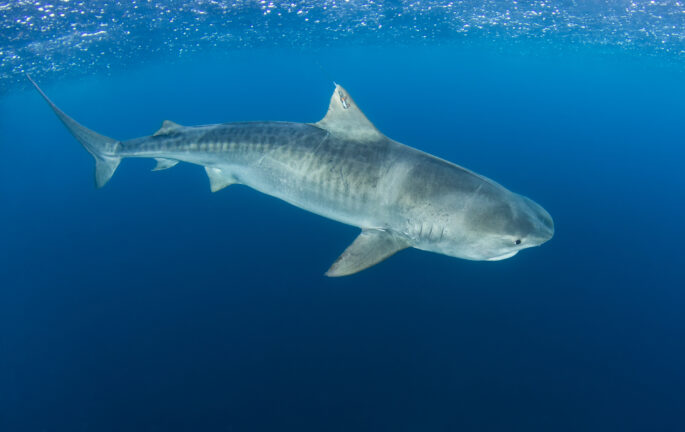
Throughout the week, the team was able to deploy five satellite tags on the dorsal fin of tiger sharks which will allow tracking of the animals over an extended period of time. The ultrasounds which were taken using high technology imagery to determine the maturity and pregnancy stage supported by Brooke Anderson, Ph.D. candidate of Dr. James Sulikowski’s Lab, Arizona State University show that the Saba Bank is a reproductive area for IUCN Near Threatened listed species tiger and the IUCN endangered listed Caribbean Reef Shark. One of the female tiger sharks was confirmed with an early stage pregnancy and boasted a total length of 251cm. This multidisciplinary research approach is necessary for taking the first steps in understanding the reproductive life cycle for the species in the region.
One of the mysteries which resulted was the first tagged male on the Saba Bank sized at 306 cm and later named Maestro Angelo. While it is common to find females, it was surprising to encounter male tiger sharks during the research. Due to the lack of research done previously on these sharks on the Saba Bank, it became evident as to why there is a need to emphasize the importance and need for scientific research into these species.
Expeditions brought forward by the protected area management organizations, such as this one, support the necessary research needed for data-driven management solutions. These results will be used to help steer future research activities, inform local governments on the significant impact these species and their habitats have on ecotourism, and ultimately strengthen conservation policies. Ayumi Kuramae, Saba Bank Management Unit Officer shared the importance of this study, “Through previous tagging expeditions it was clear that the tiger sharks tagged on the Saba Bank can travel as far south as Grenada, crossing many nations’ borders. This shows the importance of protecting the species not only in our waters, but region wide. Seeing male and female tiger sharks together of different life stages, shows us that protection of these species in our water is vital since we may be protecting the future generation of tiger sharks in the region. A decrease in the number of sharks can affect the overall fish stocks which leads to a disturbed natural balance in the sea. Saba, for example, highly depends on fisheries and dive tourism as part of the local economy which also relies on a healthy fish stocks. Thus, understanding the role of these apex predators is extremely important”.

After gazetting, the Yarari Marine Mammal and Shark Sanctuary will encompass the exclusive economic zone waters of the Saba Bank along with Saba, Bonaire and Statia. This sanctuary has the intention to provide a safe place for these animals, but without supportive data and knowledge, it is difficult to ensure they receive the appropriate protection measures. In order to survive, tiger sharks may use the Saba Bank as a key habitat for different stages of their life cycle but are known to travel to other regions during different life stages, making them a transboundary species. This expedition will help identify where larger, multi-national marine protected areas across the Caribbean should be to protect these species during their whole life cycle.
About Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance
The Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance (DCNA) is a non-profit organization created to protect the natural environment and to promote sustainable management of natural resources on the six Dutch Caribbean islands. DCNA was created to help consolidate knowledge and help bridge funding gaps for conservation within the Dutch Caribbean.
For more information on the Pregnant Tiger Shark Expedition, check DCNA’s Facebook, Instagram or DCNA’s website (dcnanature.org/news/) or contact projects@dcnanature.org